Author: Talabuyev Y.
Research shows that every business is at risk. Ransomware alone causes enormous damage, both in terms of ransom costs, which can reach tens of millions of dollars in the corporate sector, and the consequences of unplanned downtime. Additionally, natural disasters, major hardware and software failures, and other incidents can temporarily, partially, or completely paralyze a company’s operations. To quickly return to normal operations, serious preparation is required – the development and implementation of a Disaster Recovery strategy.
The issue of business recovery after IT infrastructure failures is increasingly capturing the attention of companies of all sizes. According to IDC, last year alone, companies spent a total of at least $219 billion on cybersecurity and disaster recovery solutions, which is 12% more than the previous year. These expenses are justified because a business’s ability to respond to unexpected situations determines its resilience and ability to remain competitive in the market.
Here are some additional statistics:
– The most common causes of downtime are network issues, software problems, and power outages (source: Uptime Institute).
– Following a ransomware attack, a company experiences an average downtime of 16 days (source: Coveware).
– 82% of downtimes caused by cyberattacks are due to human error (source: Verizon).
– In 2023, ransomware attacks affected 72.7% of companies worldwide (source: Statista).
– In 2024, 79% of companies plan to increase their cybersecurity budgets (source: TechTarget).
What disaster recovery includes
A disaster recovery strategy combines a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP), a Business Continuity Plan (BCP), and an Incident Response Plan. These plans cover all unplanned incidents that could potentially cause downtime, from power outages and natural disasters to cyberattacks.
Many organizations focus solely on the DRP, which details the actions to take in the event of various incidents. This plan can be developed internally within the company or in collaboration with a disaster recovery solutions provider.
Colobridge’s Expert:
“We are approached not only as a provider of expertise but also with the expectation that we will supply the computing power needed for disaster recovery, assist with selecting the optimal recovery parameters, and develop an action plan for critical situations. Why is this so important? The same issue affects different businesses in various ways. However, all companies pursue the same goals: they strive to ensure business continuity and quickly return to normal operations, avoiding prolonged downtimes. They are equally interested in minimizing the financial damage from downtimes and reducing their frequency and duration overall. Companies operating in regulated sectors, such as government or finance, and those where even a few minutes of downtime can result in significant losses, have particularly high demands.”
Key Points on Disaster Recovery Strategy
A well-developed disaster recovery strategy should consider as many potential threats as possible, describe their impacts, and propose solutions for each specific case. When creating detailed emergency response instructions, several key concepts are typically utilized, as described below.
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective): The amount of time IT systems will remain unavailable after an incident.
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective): The amount of data loss measured in time that a company can tolerate without significant damage. Essentially, it’s the data that the company can afford to lose.
- DRaaS (Disaster Recovery as a Service): A service for disaster recovery of IT infrastructure provided by a service provider, most often a cloud provider. The provider creates, manages, and maintains the infrastructure necessary to restore client services and provides the necessary software tools.
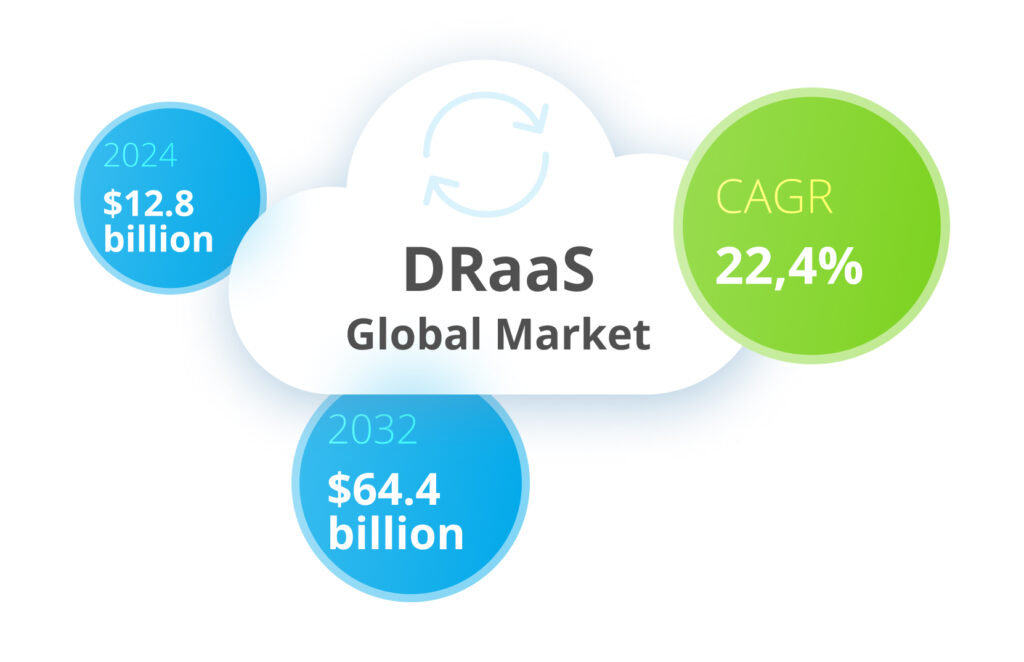
According to Fortune, the DRaaS market will reach $12.8 billion by the end of 2024 and is projected to grow to $64.4 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 22.4%. The widespread adoption of generative AI systems is one of the factors contributing to this market growth.
How to Implement a Disaster Recovery Strategy in 5 Steps
These steps are universal for any business, regardless of size or industry.
Assess the Impact of Threats
Understand how potential downtime in IT infrastructure will affect your specific business. This is done through Business Impact Analysis (BIA) — studying the consequences of various risks (cyberattacks, natural disasters, human errors, etc.) and how they will impact key business processes or the company as a whole. The business must comprehend how downtime can transform into reputational and financial losses. These include immediate losses (lost profits) and fines imposed by market regulators in certain industries.
Evaluate Risks
We have discussed the consequences of adverse incidents, but what is the likelihood of their occurrence? This can be determined through detailed Risk Analysis (RA), where each threat is separately considered along with its probability of occurring.
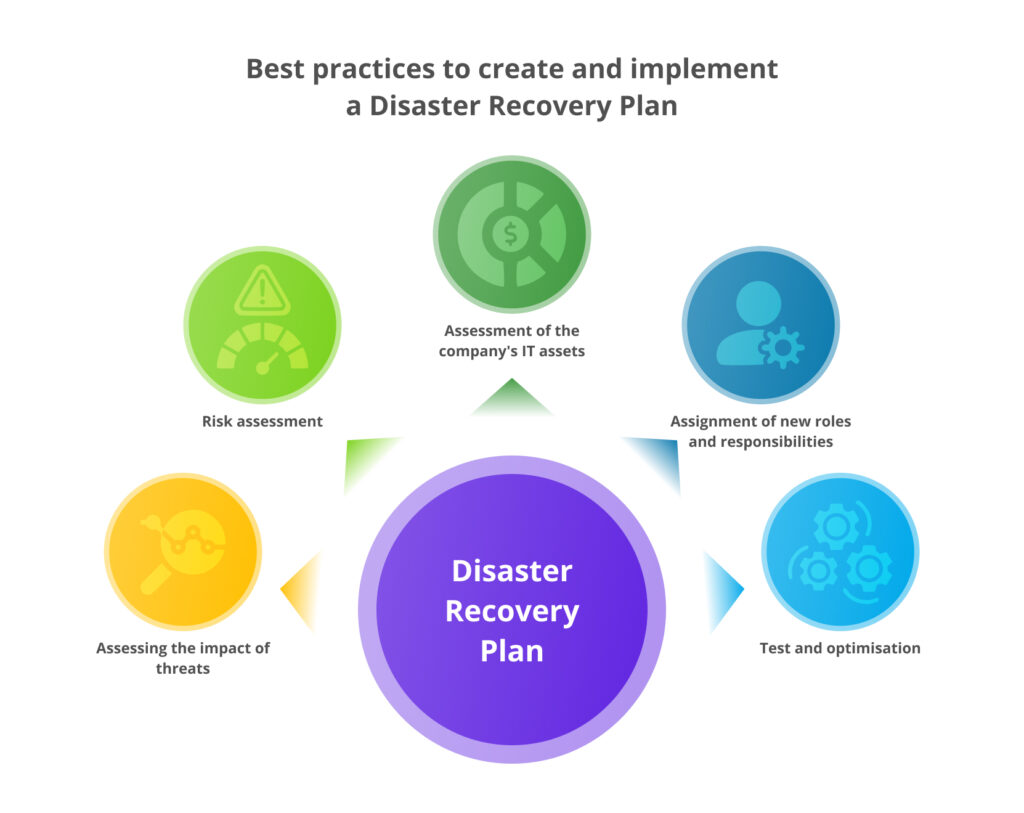
Assessment of Company IT Assets
Effective disaster recovery is possible only when a company understands the value of all its IT assets. These include computing and networking equipment, software, and everything that plays a crucial role in ensuring business continuity. It is necessary to identify the most critical, important, and secondary components. For example, critical components are those without which current business operations cannot be performed, while important components are those used by the company at least once a day.
Assigning New Roles and Responsibilities
Who will be responsible for implementing the disaster recovery plan? You need to provide a clear answer to this question and clearly outline the responsibilities of this employee. Much of the speed and effectiveness of post-disaster recovery will depend on them. In a large company, there may be several responsible individuals. For example, one employee promptly notifies top management and other interested parties of the incident. The DRP manager ensures that all those responsible for disaster recovery strictly follow instructions and act in a coordinated manner. The asset manager ensures the security of critical assets and reports on their status.
Testing and Optimization
Developing a disaster recovery strategy is not a one-time event. Even after you are convinced of its viability, it will be necessary to continuously refine and improve individual processes. At each stage, testing under conditions close to real ones will be required. This will help identify and correct errors before an actual incident occurs.
Which Solution to Choose for Disaster Recovery?
Colobridge will help you implement a disaster recovery strategy and ensure its effectiveness. A fault-tolerant platform based on two independent data centers in Germany, software from a leading global vendor in the field of backup solutions, and the expertise of our specialists will allow you to get the most out of the DRaaS service within your budget. Contact us to learn more about this product: its advantages over regular backups (this service can also be ordered from us), key features, and pricing.





