Author: Bakhmat M., Quantum Technology Analyst
This article provides an in-depth analysis of the current state and future trajectory of the quantum technology industry, drawing on the latest market data and expert insights.
- Key Insights into the Quantum Technology Industry
- How Much is Being Invested in Quantum Technology, and How Fast is the Market Growing?
- Who are the Leading Players and Innovators in the Quantum Tech Industry?
- Where are Quantum Technology Innovation Hubs Developing Globally?
- Quantum Tech Outlook: When Will Quantum Computing Become Mainstream?
- Explore Quantum Technology Further: Education and Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions about the Quantum Tech Industry
Key Insights into the Quantum Technology Industry:
- Significant Investment & Growth: The quantum market is attracting substantial investment, with projections for dramatic growth, particularly in quantum computing, which could reach $28 billion to $72 billion by 2035.
- Diverse Landscape of Players: The industry features major tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and IBM, alongside a rapidly growing number of startups specializing in hardware, software, and services.
- Global Innovation Hubs: Key regions like North America, Asia, and Europe are fostering innovation clusters through public and private funding and academic collaborations.
- Persistent Challenges: Despite rapid progress, the industry faces hurdles such as technological immaturity, high costs, scaling difficulties, and a critical talent gap.
- Long-Term Potential: While widespread adoption for large-scale applications may take another 15-20 years, useful applications for specific problems are expected to emerge sooner, promising to revolutionize various industries.
Colobridge Expert:
In the quantum industry, specific investment figures from the past year can become history overnight. For leaders, the key is not the exact number but the trajectory and scale. The trend of exponential growth in capabilities and sustained multi-billion-dollar government commitments is undeniable. Over-focusing on a single year’s decline in private funding obscures the bigger picture: the foundation for a new technological era is being laid right now. The real challenge is preparing your organization for a future that is arriving faster than annual reports can capture.
How Much is Being Invested in Quantum Technology, and How Fast is the Market Growing?
The quantum market is witnessing substantial investment flows. Total private investments in quantum technology startups reached $6.7 billion for quantum computing, $1.2 billion for quantum communication, and $0.7 billion for quantum sensing, though total investments in QT startups saw a 27% year-over-year decrease in 2023. Despite these fluctuations, investors remain optimistic about the long-term future. Public funding, however, continued strong, with governments worldwide announcing approximately $42 billion in total public funding for QT development as of 2023.
The quantum computing market is projected for dramatic growth. According to Fortune Business Insights, the market is expected to grow from $928.8 million to $6.5 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 32.1%. Further market size scenarios, including analysis by McKinsey, suggest the quantum computing market alone could reach between $28 billion and $72 billion by 2035, and $45 billion to $131 billion by 2040. This growth is part of a broader trend, with quantum technology potentially unlocking up to $2 trillion in economic value across key industries like chemicals, life sciences, finance, and mobility by 2035.
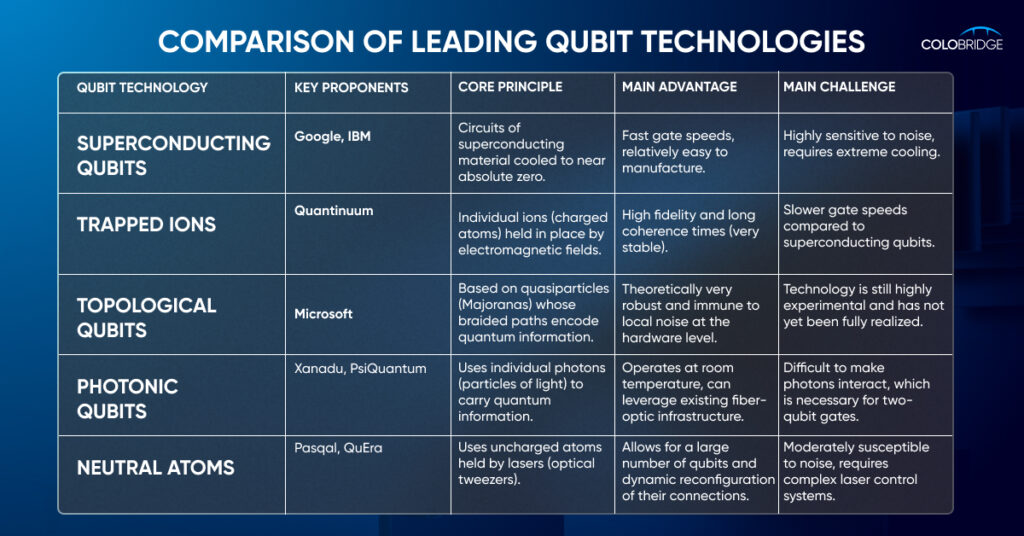
Who are the Leading Players and Innovators in the Quantum Tech Industry?
The quantum technology industry landscape includes a mix of large incumbent companies and numerous startups. Notable players actively developing hardware, software, and platforms include Google, Microsoft, IBM, and Pasqal. There are over 261 startups in quantum computing hardware, software, and services alone, with hardware manufacturers continuing to attract the most startup investment.
These leading companies are making significant strides. For instance, Google Quantum AI has introduced Willow, their latest state-of-the-art quantum chip, which demonstrates “exponential quantum error correction—below threshold!” and performed a benchmark computation in under five minutes that would take a supercomputer 10 septillion years (1025 years). Hartmut Neven, Founder and Lead of Google Quantum AI, emphasizes that Willow is a “strong sign that useful, very large quantum computers can indeed be built”.
IBM Quantum is also a major force, with a mission to build quantum computing for otherwise unsolvable problems. They have developed a powerful quantum computing stack and set an ambitious roadmap to achieve quantum advantage by 2026, targeting a large-scale fault-tolerant quantum computer, Starling, capable of 100 million quantum gates on 200 logical qubits by 2029. Matthias Troyer, IBM Technical Fellow, notes their commitment: “From the start we wanted to make a quantum computer for commercial impact, not just thought leadership”. IBM also operates 15+ utility-scale quantum systems worldwide and their Heron chip features 156 qubits.
Microsoft has carved a new path with its Majorana 1 chip, powered by a Topological Core architecture. This breakthrough leverages topoconductors to produce more reliable and scalable qubits, with a clear path to fit a million qubits on a single chip. As Chetan Nayak, Microsoft Technical Fellow, states, “Whatever you’re doing in the quantum space needs to have a path to a million qubits. If it doesn’t, you’re going to hit a wall before you get to the scale at which you can solve the really important problems that motivate us”. Microsoft’s approach aims for error resistance at the hardware level, simplifying quantum computing through digital control.
Many companies are pursuing multiple quantum technologies simultaneously, and some are offering Quantum as a Service (QaaS), allowing businesses and researchers cloud access to quantum computing power without building their own hardware.
Where are Quantum Technology Innovation Hubs Developing Globally?
Quantum technology development is happening globally, with vibrant regional ecosystems emerging in North America, Asia, and Europe. These innovation clusters are critical for facilitating close collaboration between government, academia, and industry, which is essential for advancing technology and key use cases.
- The United States leads individual countries in QT patents granted and in private funding and the number of quantum computing startups. Key innovation hubs include the Boston Area Quantum Network, Chicago Quantum Exchange, and the Mid-Atlantic Quantum Alliance.
- China demonstrates significant public investment (over $15 billion), dedicated research institutions, and increasing patent activity, particularly in quantum communication. Hefei is noted as a key innovation cluster.
- India has launched a National Quantum Mission with $730 million in funding and plans to create 21 quantum hubs and 4 quantum research parks.
- Israel has a quantum computing consortium exploring various qubit technologies, supported by $368 million in public funding.
- European countries like France, Germany, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands also have significant public funding and research hubs. The European Union and the UK have the highest number and density of QT graduates. Notable clusters include Paris (France), Delft (Netherlands), and Munich Quantum Valley (Germany).
What are the Main Obstacles to Widespread Adoption of Quantum Technology?
Despite the significant momentum, widespread adoption of quantum technology faces several hurdles. These include:
- Technological Immaturity and Cost: Quantum technology is still in early stages of development, with high costs associated with intricate cooling technologies and specialized hardware required for systems.
- Difficulty in Scaling and Error Correction: Qubits are inherently fragile and prone to errors, requiring advanced error correction techniques. While breakthroughs like Google’s Willow chip demonstrate exponential error reduction “below threshold”, and Microsoft’s Majorana 1 aims for error resistance at the hardware level, reducing the overhead of quantum error correction remains a practical challenge for large-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computers.
- Significant Talent Gap: One of the most critical challenges is the shortage of skilled professionals. McKinsey predicts that by 2025, fewer than half of quantum jobs may be filled, posing a major barrier to adoption. This highlights the ongoing need for extensive education initiatives, such as those offered by IBM, which have reached over 5.4 million learners, and Google’s Coursera course on quantum error correction.
- Lack of Standardized Benchmarks and Algorithms: While various benchmarks exist, a clear, industry-wide standard is still evolving, making it difficult to uniformly assess real-world application performance and compare across different qubit technologies. Most quantum algorithms are still theorized rather than fully implemented in quantum computers, limiting immediate high-speed operations.
Quantum Tech Outlook: When Will Quantum Computing Become Mainstream?
The current state of quantum technology is one of active development and significant investment, with a clear focus on overcoming technical challenges to realize its full potential. While experts suggest it may take another 15 to 20 years for large-scale applications to hit the mainstream, useful applications for specific problems may emerge sooner.
The long-term outlook remains positive, supported by continued growth in job postings for tech trends and heightened interest in harnessing these technologies for future growth. Quantum computing is predicted to revolutionize various industries, including medicine, finance, automotive, engineering, and cybersecurity, over the next two decades. Initiatives like DARPA’s US2QC program are actively working to deliver utility-scale fault-tolerant quantum computers, emphasizing that the horizon for transformative, real-world solutions is within years, not decades.
Explore Quantum Technology Further: Education and Resources
For individuals and organizations looking to delve deeper into quantum technology, numerous resources are available:
- Educational Resources: Platforms like Google’s Coursera offer free introductions to quantum error correction. IBM Quantum Learning also provides extensive educational initiatives, including their “Understanding quantum information and computation” series, designed to teach quantum computing fundamentals at a university level.
- Open Source Tools: Access to tools like Cirq from Google Quantum AI, and Qiskit SDK from IBM, allows developers to gain practical experience and contribute to the quantum ecosystem.
- Research and Publications: Stay informed through research publications from leading quantum AI teams, often found on their respective company websites or academic archives like arXiv.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Quantum Tech Industry
What is quantum computing?
Quantum computing utilizes the principles of quantum physics, such as superposition and entanglement, to process data using quantum bits (qubits). Unlike classical bits (0 or 1), qubits can exist simultaneously in multiple states, enabling the potential to solve complex problems far more efficiently than classical computers.
How does quantum AI differ from classical AI?
Quantum AI (QAI) integrates quantum computing to enhance machine learning algorithms, allowing for more powerful AI models that can achieve results beyond classical computers’ capabilities. This is due to QAI leveraging qubits, which can approximate multiple computations simultaneously (massive parallelism), unlike classical AI that relies on binary bits.
When is quantum advantage expected to be achieved?
While scientists are striving for quantum advantage—the ability of quantum computers to solve problems beyond classical computers—estimates vary. Some companies are projected to reach quantum advantage by 2030. However, the hardware and software for handling the most complex problems might not be available until 2035 or later.
What are some potential real-world applications of quantum computing and quantum AI?
Quantum AI is expected to revolutionize industries by accelerating drug discovery, optimizing supply chains and logistics, transforming financial modeling, and enabling advancements in materials science. It also holds promise for cybersecurity through quantum cryptographic protocols and could lead to breakthroughs in weather forecasting and automotive industries.