Author: Mykhailenko A.
Businesses utilizing cloud computing for their tasks require tools that enable monitoring, assessing usage volumes, and managing resources, services of cloud providers, and overall virtual infrastructures. This helps ensure a productive and secure environment for executing IT workloads, optimize cloud costs, and extract maximum value from it for the business. All of this can be realized within the framework of so-called “cloud management” or “cloud governance.”
- What is cloud management and how does it work?
- Challenges of cloud management
- Cloud management strategies
What is cloud management and how does it work?
Cloud management is a set of activities and approaches aimed at controlling the cloud IT infrastructure, services of providers in public, private, and hybrid computing environments. Control can be carried out both manually and with the help of automated solutions at any stage of the cloud lifecycle: from provisioning cloud resources by the provider and deploying IT systems in the cloud to decommissioning them.
The role of cloud management and why it is important
- businesses receive a flexible cloud infrastructure in which computational resources are available in the necessary volume and are properly distributed among IT workloads;
- a significant portion of cloud service-related processes, such as resource reallocation and monitoring, are either automated or delegated to the service provider;
- the information obtained through the supervision and management of cloud data allows for making informed decisions regarding cloud cost optimization without compromising performance.
Colobridge’s Expert:
“The ideal scenario is when the client knows which cloud resources are currently in use, has a full understanding of cloud costs, and is confident that any issues will be quickly resolved. For example, virtual machines are automatically restarted after a failure, the provider promptly allocates additional resources during rapid workload growth, and backups, which are regularly created and sent to storage, can be restored in a short time. Cloud management methodology undoubtedly plays a significant role in this. However, the choice of provider is also important – one that can provide certain guarantees of data availability (as fixed in the SLA) or provide reliable tools for automated backup creation.
As a cloud service provider, we understand the desire to use Cloud Management Platforms (CMP) that allow managing multiple different cloud environments simultaneously. Many companies do not limit themselves to just public or private clouds, but build hybrid and multi-cloud environments – in their case, using CMP would be a reasonable and economically justified solution.”
Cloud management features
Cloud management functions include managing data and applications stored in the cloud, as well as clouds of different types and from different service providers.
- automation of processes aimed at redistributing computational resources with minimal human involvement, thereby reducing operational load;
- maintaining a level of control over workloads in the cloud that is familiar to on-premises environments. Adherence to internal and industry security requirements;
- logging actions in the cloud to promptly respond to failures and errors in virtual infrastructure operation. Automatic incident response;
- transparent management of cloud costs and forecasting them in the short and long term.
Key components of cloud management:
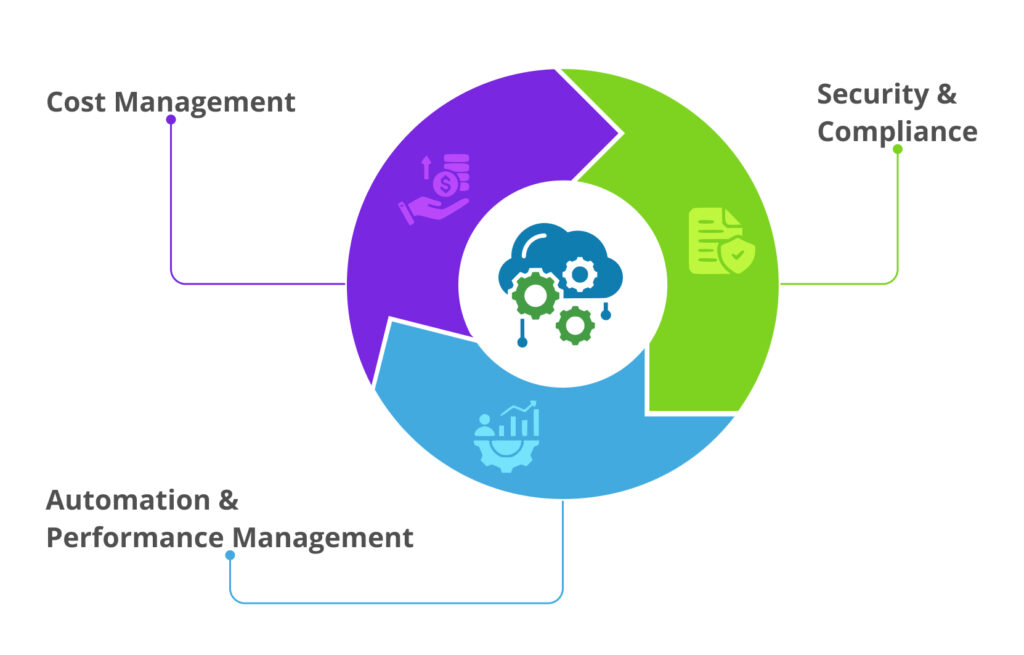
Challenges of cloud management
Transitioning to a cloud management model may come with a range of challenges, including:
- clear understanding of the client’s responsibility for security issues and ensuring them in all aspects of working with a single cloud or multiple cloud providers;
- optimization of cloud expenses in the short and long term, considering current needs and future scalability of IT infrastructure to avoid excessive resource allocation by the provider;
- compliance with corporate and industry requirements, especially when dealing with sensitive data such as medical, biometric, financial, and others;
- automation of various processes, which may require additional resources and face resistance within the team due to concerns about job displacement by employees.
Cloud management strategies
Haphazard use of monitoring, proactive response, and business process automation tools may not lead to the desired outcome. That’s why it’s crucial to develop a cloud management strategy and implement it step by step. To do this:
- cover all cloud environments with monitoring and control tools and begin centrally managing the collected data;
- continuously track any changes that may impact the availability, performance, and security of your IT systems;
- analyze the data obtained from monitoring to promptly identify potential issues, violations, and incidents that could lead to serious losses in the future.
Get advice on security management capabilities, cost optimization, IT infrastructure migration, and other aspects related to building cloud IT infrastructure by reaching out to Colobridge company managers.





