Author: Volnyanskyi A.
The open-source language model DeepSeek-R1 rapidly became one of the most popular globally, causing Nvidia’s market value to plummet by $600 billion and directly competing with ChatGPT. Meanwhile, Alibaba Cloud released Qwen 2.5—one of China’s top AI models, ranking third globally behind Anthropic and OpenAI. These examples highlight China’s swift advancements in AI, underscoring its rising competition with Western counterparts. The industry’s rapid growth is remarkable, drawing significant attention from major market players and end-users alike. This article explores the industry’s evolution and identifies the pivotal Chinese AI projects currently transforming the landscape.
- The Evolution of Chinese AI
- Main drivers behind the growth of China’s AI market
- Key Projects in Chinese AI
- Alibaba and the Qwen Model
- Tencent and Hunyuan Integration in WeChat
- Baidu and Ernie Bot
- ByteDance and the Doubao Chatbot
- DeepSeek — the Ambitious Chinese AI Making Waves
- SenseNova by SenseTime
- SparkDesk by iFlytek — Leading the Voice AI Race
- Moonshot AI and the Kimi Chatbot
- The Dark Side of Chinese AI: Censorship, Regulation, and New Workforce Challenges
- Impact of Chinese AI Projects on the Global Industry and Domestic Market
The Evolution of Chinese AI
China’s AI journey began over 50 years ago, following Deng Xiaoping’s economic reforms, which positioned science and technology as the primary drivers of national productivity. Initially, Chinese AI progressed slowly, hindered by a lack of resources and expertise, making local developments notably inferior to Western standards. However, the situation began changing dramatically after the early 2000s. In 2016, China declared its ambition to become the global AI leader by 2030, and by the start of this decade, it had already secured the top spot worldwide in terms of AI research publications and AI-related patents.
How does the current global AI landscape (including Chinese AI) look today?

Several “national AI teams” currently operate in China, uniting around fifteen companies and startups involved in artificial intelligence development. Together, they’re covering all the most promising areas of AI.
Main drivers behind the growth of China’s AI market
Government support. The Chinese government invests heavily in the sector, and even though it’s fairly regulated overall, this hasn’t stopped quick adoption of innovation and attracting investment. At the same time, the country blocks Western technologies to eliminate competition.
US sanctions. The US restricted Chinese access to Nvidia’s chips—the global leader in AI GPUs (especially A100 and H100). This opened up opportunities for local firms; for example, Huawei developed its own Ascend 910C chip, competing directly with Nvidia’s offerings.
Massive market. Over 1.4 billion people represent potential users for Chinese AI applications, offering unique opportunities for technology scaling and extensive data collection to train neural networks.
However, certain factors hold back growth. For instance, the local labor market, dominated by agriculture, manufacturing, and construction, is harder to automate through AI due to the significant share of physical labor.
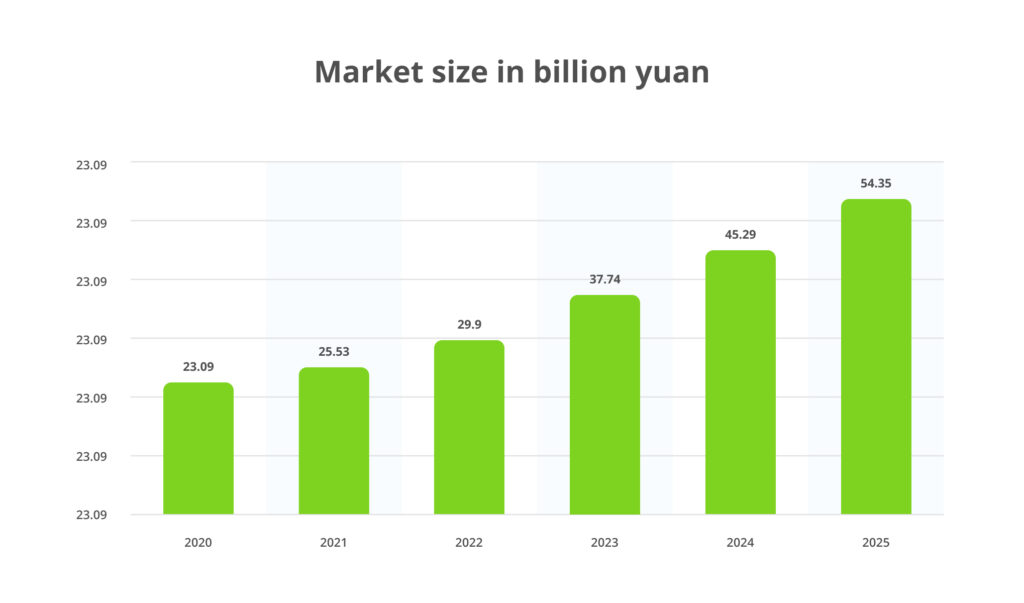
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1560400/china-ai-software-market-size/
Key Projects in Chinese AI
Let’s dive into some major achievements by Chinese AI companies and key milestones associated with these projects.
Alibaba and the Qwen Model
Alibaba continues developing its Qwen series of large language models. In January 2025, the company introduced Qwen 2.5-Max, built on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture and trained on over 20 trillion tokens. Qwen 2.5-Max shows impressive performance in math, programming, and general tasks, competing head-to-head with DeepSeek-V3 and GPT-4o. Last November, Alibaba released QwQ-32B, a 32-billion-parameter model with a 131,000-token context window. Despite being smaller, its efficient architecture and reinforcement learning training make it comparable in performance to larger models.
Alibaba Group continues investing in AI and cloud technology, recently announcing an additional $53 billion investment in these areas over the next three years.
Tencent and Hunyuan Integration in WeChat
Tencent has integrated its Hunyuan model into over 200 Chinese AI services, including WeChat (Weixin). WeChat also uses DeepSeek-R1, another prominent Chinese AI, to power its AI Search function. In February of this year, Tencent opened full public access to its language model Hunyuan T, capable of interpreting multi-dimensional questions and their underlying logical connections. Just a few days later, the company announced Hunyuan Turbo S, a model known for responding to queries within one second, setting it apart from other AI models like DeepSeek-R1 or Hunyuan T1, which typically require “a moment to think.”
Baidu and Ernie Bot
Baidu announced Ernie Bot as its response to ChatGPT two years ago and has significantly enhanced its reasoning capabilities, creativity, and memory since then. The bot exceeded 300,000 downloads on the App Store on its first day and today handles millions of requests daily, including those from the Chinese government. Ernie Bot is deeply integrated into Baidu’s search engine and cloud services.
In 2025, Baidu’s Ernie Bot will become freely accessible to all users without restrictions on device types. Developers also plan to open-source Ernie’s code and introduce the new Ernie 5 model, featuring multimodal processing capabilities across text, video, audio, and images.
ByteDance and the Doubao Chatbot
Last year’s launch of Doubao caused significant excitement among Chinese AI users. The new app quickly surpassed Ernie Bot in downloads, becoming China’s most popular AI chatbot. Doubao is deeply integrated with TikTok and Douyin, offering content generation, data analysis, and online search. Its standout feature, however, is personalization: users can adjust chatbot behaviors, communication styles, and train it on personal datasets for more accurate responses.
In early 2025, developers introduced the next-generation language model, Doubao-1.5-Pro, featuring enhanced reasoning capabilities. ByteDance is currently developing its own AI chips to reduce reliance on third-party suppliers.
DeepSeek — the Ambitious Chinese AI Making Waves
DeepSeek is China’s fastest-growing open-source AI, directly competing with global heavyweights. Its capabilities are comparable to GPT-4o, yet the startup trained its model for less than $6 million—significantly cheaper than its Western counterparts. DeepSeek’s rapid success caused a notable drop in Nvidia and Microsoft stock prices and quickly caught the attention of the Chinese market. Companies from diverse sectors like finance, pharmaceuticals, and automotive have started integrating the DeepSeek R1 model into their applications. Its emergence also sparked massive investment flows into the Chinese AI space, inspiring ambitious startups racing to create the “next DeepSeek.”
SenseNova by SenseTime
SenseTime is a leading developer in facial recognition and video analytics, also known for creating some of China’s strongest AI models. Its previous LLM, SenseNova 5.5, enabled real-time multimodal interaction, enhanced performance, AI-avatar video generation, and integration with tools like Code Raccoon and Office Raccoon (optimizing coding and office tasks). Introduced in early 2025, the SenseNova Unified Large Model rapidly topped key benchmarks, showing exceptional strength in language and visual tasks, and secured first place in China according to the SuperCLUE Chinese Large Model Benchmark Report.
SparkDesk by iFlytek — Leading the Voice AI Race
iFlytek is a top developer of speech recognition and speech synthesis technologies in China, with its SparkDesk AI competing head-to-head against OpenAI’s Whisper and Google’s Speech-to-Text. The latest model, SparkDesk 4, receives outstanding benchmark scores and continues expanding its ecosystem with millions of developers. It handles conversations in 74 languages and accurately recognizes and transcribes speech even in noisy environments.
Recently, iFlytek partnered with Huawei to launch OceanStor AI Storage, designed for AI data storage and processing. Meanwhile, Feixing №1 remains China’s first ultra-large computational platform used for training massive AI models with trillions of parameters.
Moonshot AI and the Kimi Chatbot
Moonshot AI specializes in developing language models and enterprise-level AI solutions, actively drawing investment, raising $1 billion in the past year alone. Their latest chatbot, Kimi 1.5, was announced in January 2025. The company claims the new version matches OpenAI’s o1 in mathematics, coding, and multimodal reasoning tasks. Other standout features of Kimi 1.5 include uploading up to 50 files of various formats, strong logical reasoning performance, and fully open-sourced code available on GitHub.
Comparing Key Projects in Chinese AI:
| Company | AI Product | Primary Function | Key Technologies | Distinctive Feature |
| Alibaba | Qwen 2.5-Max | Language model competing with GPT-4o; strong in math and coding | Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), trained on 20T tokens | Massive token count, high performance |
| Tencent | Hunyuan | Powerful language model integrated into WeChat for quick response and analytics | Deep integration into WeChat, rapid query processing | Instant response speed |
| Baidu | Ernie Bot | Popular chatbot deeply integrated with Baidu’s ecosystem | Multimodal processing across various content types | Deep integration into Baidu ecosystem |
| ByteDance | Doubao | Personalized chatbot integrated with TikTok/Douyin | Personalization, data analytics, online search | Highly customizable and personalized |
| DeepSeek | DeepSeek R1 | Open-source model competing with GPT-4o at low training costs | Efficient training, cost-effective methods | Most cost-efficient Chinese AI to train |
| SenseTime | SenseNova | Multimodal model for facial recognition and video analytics | Video generation, integration with Code Raccoon and Office Raccoon | Leading multimodal and video analytics AI |
| iFlytek | SparkDesk | Leading voice AI competing with OpenAI Whisper | 74 languages, speech transcription & synthesis | Leader in voice AI, high accuracy |
| Moonshot AI | Kimi 1.5 | Logical reasoning chatbot, supports file uploads, open-source | Logic handling, uploads up to 50 files, web browsing | Open-source, supports various data formats |
The Dark Side of Chinese AI: Censorship, Regulation, and New Workforce Challenges
Chinese AI often sparks discussion around its impact on the labor market, ethical implications, and heavy government regulation. Local AI developments are indeed subject to strict censorship and tight control over generated content. For instance, the DeepSeek-R1 model has faced criticism for internally censoring politically sensitive topics, such as the 1989 Tiananmen Square incident. This censorship reflects the reality that the Chinese government not only supports but also closely regulates and strictly controls the AI sector. Legal norms were enacted to prevent the generation of sensitive content that could threaten the existing regime, incite separatism, promote the overthrow of socialism, or undermine national unity.
Another critical dimension of China’s AI evolution is its impact on employment. Primarily, this is reflected in decreasing demand for low-skilled laborers, especially migrant workers, as companies shift toward smart manufacturing, robotics, and automation systems. However, this labor issue may naturally resolve in the near future: China’s population is rapidly aging, and the size of the active workforce is shrinking. In the long run, widespread AI adoption could become a natural solution to China’s demographic challenge.
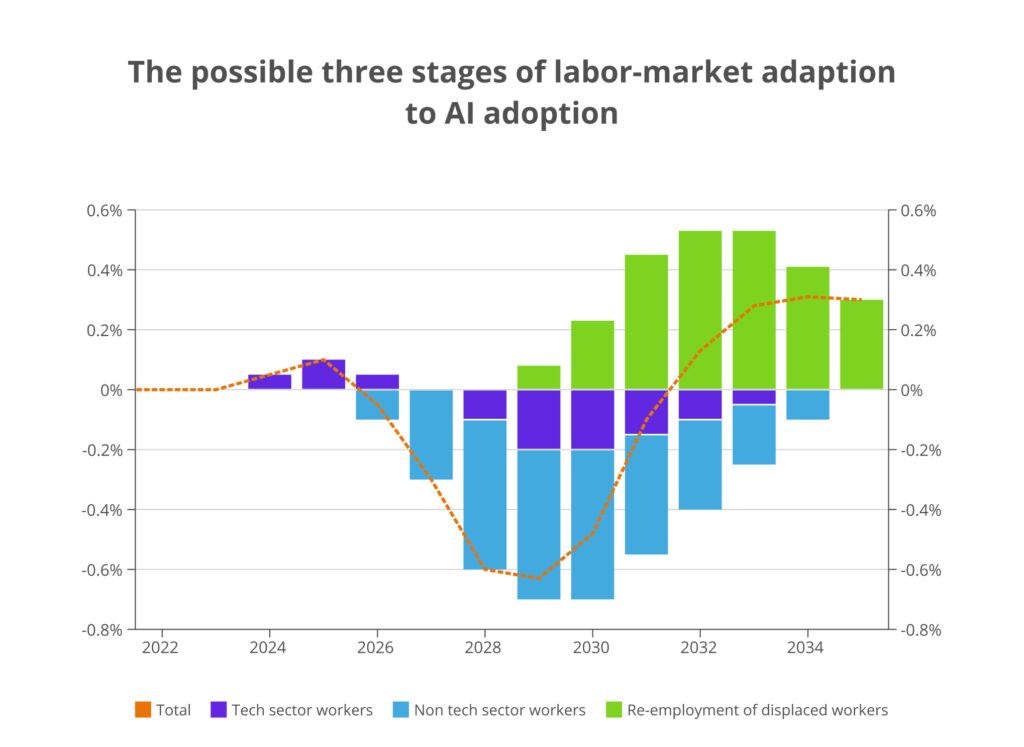
https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/articles/what-advanced-ai-means-for-chinas-economic-outlook
Impact of Chinese AI Projects on the Global Industry and Domestic Market
We’re currently witnessing a significant impact of Chinese AI initiatives on the global industry. The rapid growth of China’s AI sector has become a serious competitor to American technology, prompting the creation of the National Security Commission on Artificial Intelligence (NSCAI), which identified Chinese AI developments as a threat to US technological supremacy. Moreover, Chinese companies, often closely linked to the government, have long faced accusations of cyber espionage and intellectual property theft. In response, the US and subsequently other countries began restricting access to Chinese AI technologies. Texas was the first US state to ban DeepSeek, citing concerns over potential leaks of user data to the Chinese Communist Party. Similar measures and investigations into data protection compliance were initiated by Italy, Australia, Taiwan, and South Korea.
Despite sanctions and heightened oversight, China continues to solidify its AI position, aggressively integrating AI solutions into industry, finance, and healthcare. Strategic investments, vast data access, and robust infrastructure have allowed China to scale its AI solutions rapidly, challenging Western dominance. The key developments in Chinese AI over the past year confirm that this strategy has proven successful.
According to Goldman Sachs Research, the emergence of new AI models within China is expected to accelerate technological development and boost the country’s GDP growth. China has already surpassed the EU and the UK in the number of foundational AI language models. The arrival of DeepSeek—developed at significantly lower costs—suggests faster technology adoption and economic expansion. By 2026, generative AI in China could speed up economic growth significantly, and by 2030, it might contribute an additional 0.2–0.3 percentage points to GDP, surpassing earlier projections of just 0.1 points.
Goldman Sachs Research also forecasts that the adoption rate of Chinese AI across various sectors will exceed the anticipated 30% by 2030, reaching its peak in the early next decade. If this prediction proves accurate, China’s AI integration—in terms of speed and depth—will rival the world’s largest economies.