Author: Volnyanskyi A.
We continue to introduce you to the CRM framework, which involves managing customer relationships based on data. Previously, we covered data management principles, and now we move on to one of the most intriguing topics: analytics. Our article explores why advanced analytics, particularly predictive and descriptive, is replacing traditional analytics and what tasks it solves in marketing.
- Traditional Analytics or Advanced Analytics?
- How advanced analytics helps improve customer relationships
- Types of analytics
- How to use advanced analytics in business
Traditional Analytics or Advanced Analytics?
Today’s customers expect a more personalized shopping experience than ever before. And no, this isn’t just about addressing them by name in email newsletters or listing products frequently purchased in their chosen category. Traditional analytics provides a superficial understanding of sales and customers. It can tell you how many products, in which categories, and for what amount you’ve sold, or which advertising campaigns were most effective. However, it doesn’t allow you to predict customer desires or influence their future purchasing behavior. This is where advanced analytics comes into play. It is already being hailed as a powerful tool capable of extracting maximum value from data and directly impacting a company’s revenue.
You can utilize advanced analytics within the CRM framework, which is based on building data-driven communication with customers. Companies already using this approach see a return on investment (ROI) in marketing that is 5-8 times higher. Additionally, 9 out of 10 marketers (87% according to Invesp) consider data one of the most undervalued assets, while 73% of customers (according to Salesforce) expect companies to consider their unique preferences and strive to meet them.
How advanced analytics helps improve customer relationships
The value of information increases when it becomes a source of new knowledge. Advanced analytics enables this transformation by identifying correlations between data and modeling predictions, which allow for precise decision-making based on customer behavior and preferences.
What role does the analytical system play?
- Creates a 360-degree view of the customer by analyzing their profiles and actions, revealing patterns that are not obvious to humans. This information helps predict future actions, such as identifying customers who are likely to leave the company and pinpointing the factors that most strongly influence churn.
- Determines the quality of content, chosen communication channels, and marketing campaigns. This helps understand which customers are more engaged and who performs the desired actions (places an order, subscribes to new product updates). The quality of marketing campaigns is assessed in terms of incurred costs. Additionally, it is possible to track the main sources of traffic and identify the most effective types of campaigns.
- Provides recommendations for improving communication strategies using micro-segmentation (advanced segmentation), which takes into account significantly more factors compared to traditional segmentation. This includes not only historical data but also forecasts of customer value, complex behavioral, demographic, and transactional profiles, communication preferences, and much more. Micro-segmentation allows for a better understanding of the target audience, its values, and preferences, forming the basis for creating detailed buyer personas and choosing the appropriate channels for delivering messages.
Types of analytics
Earlier, we used the term “advanced analytics” without specifying what it entails. There are several types of analytics, and for a business to get the most out of its data, it’s important to understand the capabilities of each.
Descriptive analytics: This type describes events that have occurred in the past. For example, it allows you to calculate the revenue generated by a customer for the company, the number of purchases made over a selected period, or the number of new customers brought in by cold calling.
Predictive analytics: This type predicts behavior based on historical data. At this stage, statistical algorithms and machine learning are involved, helping to make accurate predictions about future events based on past occurrences. For example, it can determine which communication channel with the customer will be optimal, which offer they are most likely to take advantage of, what average check and overall profitability the company can expect, and which customers it might lose in the near future.
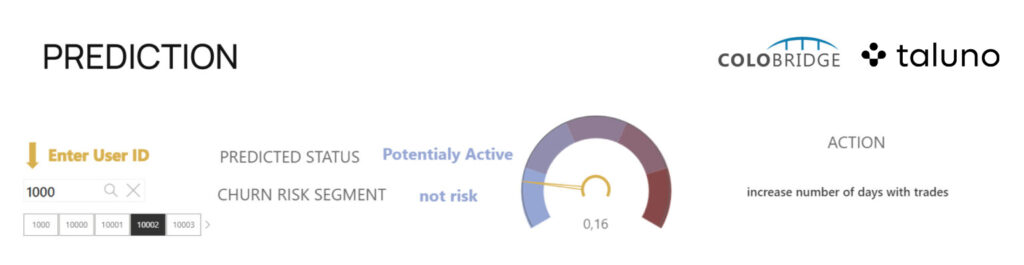
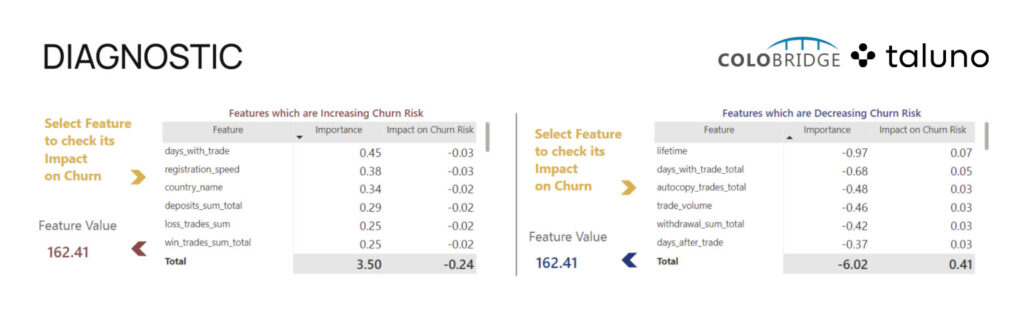
Diagnostic analytics: This type describes the reasons behind specific events and can be used to influence them before they occur. Diagnostic analytics helps understand the challenges a customer faces when using a product and what needs to be changed to make the experience more positive. Ultimately, this can help increase the company’s profitability by enhancing the customer’s lifetime value.
How to use advanced analytics in business
Today, it is incredibly challenging to build an optimal customer relationship system without leveraging analytics and ignoring the necessity of data-driven business decisions.
Here’s what a company can do to benefit from analytics:
- Start collecting data: Transform raw data into valuable business insights.
- Utilize machine learning: Predict customer actions and make data-based decisions.
- Implement reporting tools: Visualize complex data for better understanding.
- Develop a system: Create personalized messages that enhance customer service quality and increase organizational revenue.
Reach out to the specialists at Colobridge and our subsidiary project Beinf.ai to explore the potential of data utilization (our product Opportunity Audit) and receive recommendations that will elevate your customer interactions to the next level.
