Over the past few years, Hybrid Cloud has been significantly outpacing Public Cloud and Private Cloud when it comes to annual growth rates. The same goes for placing and renting physical hardware as these services are becoming less and less appealing to customers due to constantly rising expenditures. This article explains what hybrid cloud infrastructure is, why it is becoming more and more attractive to corporate clients, and in which scenarios it will prove itself best.
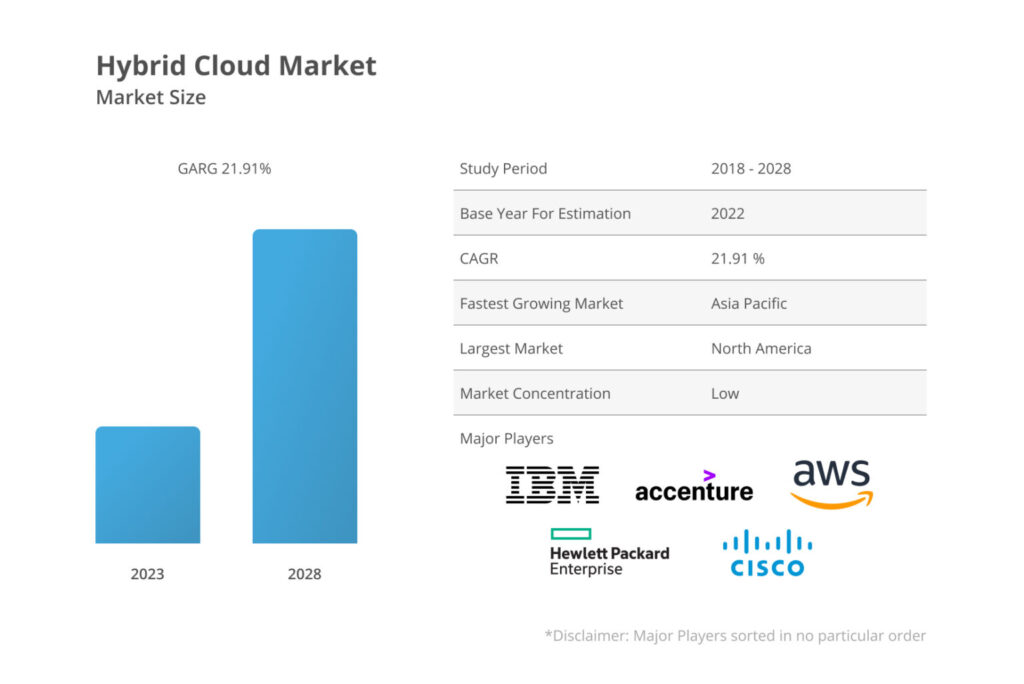
Hybrid cloud market is indeed showing impressive growth, and this trend is likely to continue over the next few years.
- Definition of hybrid cloud
- Hybrid cloud advantages
- Disadvantages of hybrid cloud
- Hybrid cloud best practices
Definition of hybrid cloud
What is IT infrastructure for a company? It is a set of computing resources that support a number of business tasks and play a fundamental role in ensuring overall business continuity for many companies. Different companies choose different service consumption models: some are satisfied with virtual resources in public clouds, others prefer private clouds, and some prefer local data storage. The second and third options are typical server solutions that are often used to contrast cloud solutions (the first option).
Thus, hybrid cloud approach is a combination of several models of using computing resources within one client infrastructure. In practice, it can be one type of cloud (e.g., IaaS, “Infrastructure as a Service”) and a local data сenters or any other combination of cloud and physical resources.
What are the components of hybrid cloud?

Hybrid cloud infrastructure can only be defined when separate cloud and server models of using computing services are interconnected and work in synergy. Several technologies are used to establish interconnections: VPN (virtual private network), WAN (wide area network), and access to APIs (application programming interface).
Colobridge’s Expert:
“Hybrid cloud infrastructure is used when one model only – server or cloud one – cannot fully meet the needs of the business. For example, public cloud is well suited for, say, retail with its peak loads or test environments, but at the same time, it is hardly suitable for running high-load databases or ERP systems. It is in the second case that it is advisable to build a hybrid model: a fixed high-performance part for static loaded systems is placed on your own platform or in a private cloud, and the flexible part of the infrastructure for dynamically changing services is transferred to the public cloud. Moreover, such a model is often used to meet regulatory requirements: whatever cannot be transferred to the cloud or must meet a certain specification is stored on-premise, while the remaining IT services are migrated to the public cloud.”
Hybrid cloud advantages
The most important thing when it comes to hybrid cloud services is that they make it possible to combine the benefits offered by cloud and server solutions within a single IT landscape. Hybrid cloud integration allows businesses to optimise the maintenance costs involved, efficiently store different types of data and scale easily.
- Best possible load distribution. Public clouds are perfect for launching temporary projects, quickly rolling out new IT products, and expanding computing capacities at peak demand times (e.g., during the high season or marketing activities).
- Reduced IT infrastructure costs. This stems from the previous point – the company pays only for the amount of resources in the cloud it actually received from the service provider.
- Secure performance of critical workloads. On the one hand, the company has the cloud with all its advantages, and on the other hand, it has its own data сenters or private cloud where the most critical business data will be stored in accordance with the requirements set by the internal security service and market regulators.
- Easy scaling. Unlike purely server-based infrastructure, computing resources and storage space in the cloud are easy to obtain almost instantly and in unlimited amounts.
- Disaster recovery through competent load balancing. The main thing is to implement this feature at the design stage: if a server or a cluster of servers fails at the client’s platform, key IT services will still run in the cloud.
Business continuity can also be ensured by other means, such as DRaaS (Disaster Recovery as a Service), which enables a failover solution at infrastructure level. In this case, its functionality will be restored in the cloud, at Colobridge’s backup facility, within a short period of time – 20 minutes or more after the incident.
Disadvantages of hybrid cloud
Despite the fact that the solution is popular and flexible, it still has some drawbacks:
- challenges in integrating local infrastructure with the cloud one;
- difficulties associated with maintaining and managing a private cloud;
- uneven load on cloud and server parts of the IT infrastructure;
- infrastructure complexity may increase unpredictably with scaling.
Although all these drawbacks seem quite significant, almost most of them can be avoided when designing a hybrid cloud. To achieve this, all you need to do is choose a service provider carefully – its experience, relevant expertise, and client-oriented approach will help you avoid negative situations when using hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud best practices
Based on our experience, renting hybrid cloud infrastructure is most interesting for companies that meet the following descriptions.
- Companies comply with regulatory and/or internal security requirements limiting the use of public clouds. In this case, the most sensitive information is stored in the corporate data сenters (locally on the client’s side), i.e. the information which could lead to undesirable consequences if disclosed or modified, and the rest of the data is stored in the public cloud.
- Companies want to ensure faster access to the server for certain client applications. In this situation, it makes sense for a company to rent cloud resources in a data сenters that is geographically close to its customers in addition to its local facilities. This is relevant when it is necessary to automate production, deliver multimedia content quickly, deploy a gaming platform or a platform for using augmented reality technologies.
- Companies seek to make their IT infrastructure more fault-tolerant. To do this, they place database backups and other backups in the cloud (BaaS, “backup as a service”), allowing the company to continue operations if a critical situation occurs.
- Companies are planning to migrate their entire IT infrastructure to the cloud, but want to split the process into several stages. In this case, hybrid cloud model makes it possible to get personalised experience of using cloud products and in the future migrate the load as desired.
Examples of hybrid cloud can most often be found in the following areas:
Colobridge experts will help you migrate to a hybrid cloud infrastructure: they will audit your current workloads, take into account the specifics of your business loads and security requirements, draft a concept and plan migration of individual IT services to the cloud. With us, you’ll build a high-performance, fault-tolerant and customised hybrid cloud that meets your real needs.





