IaaS, SaaS and PaaS are all clouds available to users as a Service. Understanding their differences, potential and key limitations is important in order to choose the cloud solution suitable for the business needs a particular company has.
Common principles cloud services operate on
As any other computing environment, cloud is based on hardware resources. Hypervisors controlled by the orchestrator are installed on the hardware.
- A hypervisor is software that isolates guest virtual machines, emulates virtual devices, and enables multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on the same hardware.
- Orchestrator is a management system and a key cloud component that manages hypervisors and abstracts away from the hardware the virtual machines running on it.
On-premise is the evolutionary model preceding cloud. On-premise means that physical hardware and the software deployed on it are on the client’s premises: in the office or, if the company is mature enough, in its own data center.
In cloud model, servers operate in a single system where their computing and other resources are first combined and then distributed among virtual machines (VMs). At the same time, users do not know on what hardware the cloud is deployed, they will never have to scale physical infrastructure, look for new components, resolve compatibility issues and check the timeframe of warranty service.
Allocating resources is somewhat similar to Smörgåsbord: everyone can request a virtual machine for themselves that has a certain processing power, the required memory and storage capacity, and the data transfer channel bandwidth. Although there are also maximum (and most feasible) VM configurations, this is a much more flexible resource allocation model, unlike a physical server. Its resources are very limited and scaling them is expensive and time-consuming.
The rationale behind opting out for cloud services
Clouds enable hosting almost any system and application as long as it is in line with company security policies. Corporate clients are primarily interested in the following opportunities provided by virtual IT infrastructure:
- remote access to data from anywhere in the world provided there is Internet connection there;
- delegating administrative tasks to the provider in part or fully;
- reduced payroll costs in respect of full-time administrators;
- no need to purchase hardware, software and licenses;
- in most cases, fast scaling is available if there is a dramatic load increase;
Let’s take a closer look at each of the three popular cloud service models.
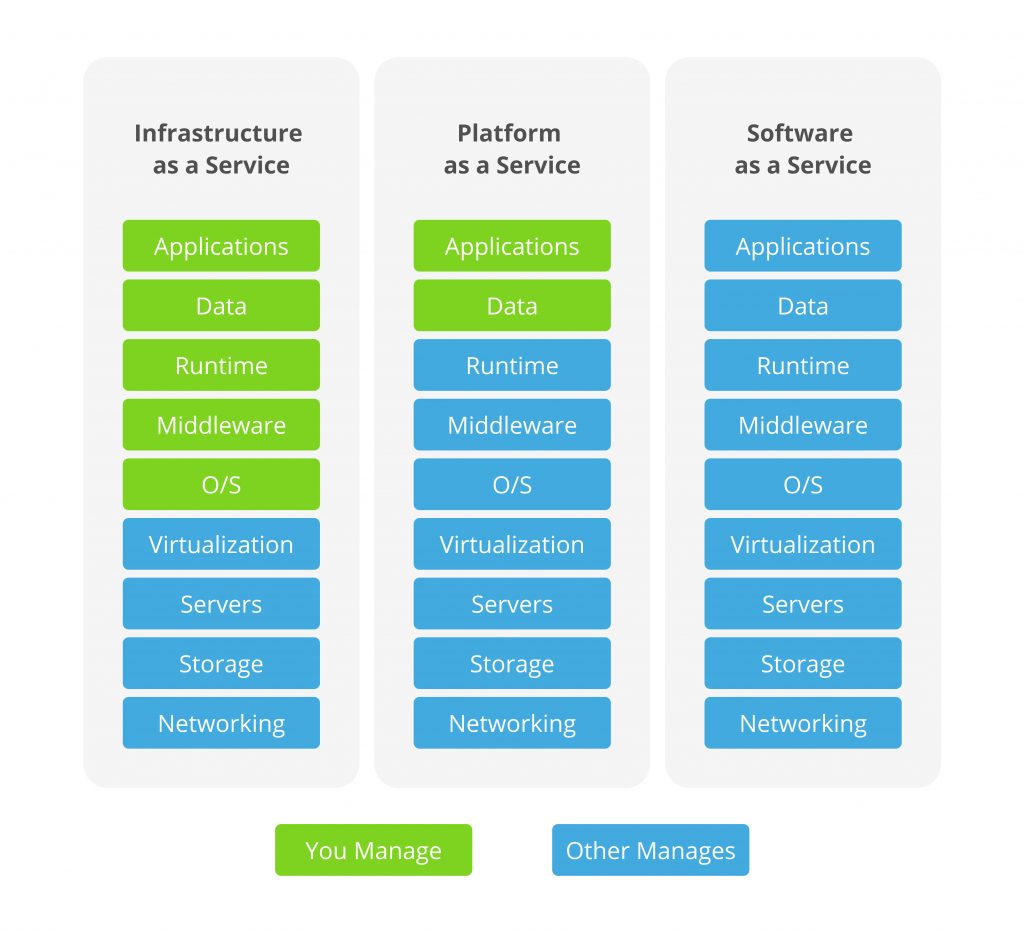
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
In IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), the client gets a pool of computing resources in the cloud at his/her disposal: a certain processing power, memory, disk space, a data transmission channel. Together, it constitutes a virtual analogue of the physical infrastructure – the so-called virtual data center where the client independently selects the server parameters tailored for specific tasks, combines the parameters in a network, installs operating systems and applications. Everything related to hardware and hypervisor operations remains within the provider’s responsibility; the client only gets access to the OS s/he installed from scratch or a pre-prepared template.
IaaS covers:
- virtual resources from which the client can put together the number of virtual servers he needs and, if s/he wants, combine them into a network;
- a cloud resource and network access management system, a basic monitoring system as well as tools for remote access to the server console (for creating and editing virtual machines);
- virtual storage with performance parameters adequate for the client’s tasks;
- automatic backup and restore tools that protect against data loss if there should be a failure.
IaaS virtual cloud is adequate for hosting online stores and corporate portals, it can be used to arrange storage (for example, to place accounting databases), deploy CRM or ERP, a terminal or mail server, arrange a remote office, software development or testing environment, as well as to implement many other software solutions. Also, part of the infrastructure can be migrated to cloud if local servers capacity is not enough to carry out current business tasks.
Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Google Computing Engine are global IaaS providers. Ukrainian customers can get this service at Colobridge on more favorable terms: with 24/7 technical support, staff speaking their native language and available through several communication channels.
Benefits of using IaaS
It enables a quick launch of a business that initially does not have its own IT infrastructure or the one that used to have local or rented physical infrastructure to solve its own tasks only.
Saving on IT infrastructure maintenance and development. The company does not need to pay rent for premises, buy, maintain and upgrade hardware, license software solutions, employ several system administrators, and invest in scaling computing systems.
The provider is responsible for infrastructure stable operation. It provides the client with a data center that has already been built with a full range of related services (climate control, data transmission channels, fire protection, etc.); it also manages all engineering systems and maintains their stable operation. The client knows that the resources provided to him/her will be available under SLA (service level agreement) and does not deal with hardware-related problems: breakdowns, moral obsolescence, normal wear and tear, overheating, etc.
Flexible response to rapidly changing loads. The influx of customers during the sales season in an online store, the surge in the number of people who want to go to the cinema together with the whole family during the Christmas and holiday season are the examples of when a company may have a drastic change in terms of the resources required. A virtual capacity pool in IaaS can be ordered in a couple of hours, whereas on-demand scaling takes just a few minutes.
It is worth noting that management options open for the client within IaaS modality are rather limited since s/he does not get access to either hardware or hypervisor. The client can only change the configuration of computing resources, install software, control the operation applications with monitoring tools and connect other services by the provider as per the service model.
PaaS: Platform as a Service
In PaaS (Platform as a Service), the client receives cloud resources and a set of tools that are pre-installed, configured and fully prepared to be used to perform various tasks. Such tools can cover DBMS, environments for analyzing big data or processing results obtained from industrial IoT sensors. The client does not have to develop them from scratch – it is enough to start using what is already there on the platform. At the same time, access is made available only to platform interfaces, while the provider sets up virtual servers and the OS itself.
PaaS is considered one of the best environments for working with databases: the client just needs to choose any of the DBMS offered by the provider, configure it and upload the data. PaaS is also adequate for container development, machine learning-based applications, and analytics using tools like Hadoop or Spark from Apache.
A software developer is a typical user of “platform as a service”.
Benefits of using PaaS
- The provider is responsible for developing, updating, correcting and maintening the tools on the platform.
- The client saves on software development and configuration and can quickly start using the necessary tools.
- The standardized developer tools available on the platform can be easily combined in any way depending on the client’s tasks.
Despite the fact that IaaS and PaaS are cloud services, in the second model, the client cannot quickly scale his/her IT infrastructure and have major influence on its configuration.
SaaS: Software as a Service
In SaaS (Software as a Service), the client gets a customized ready-to-use software solution that requires no scaling or configurations. The vast majority of corporate and private users are well aware of SaaS clouds since this model is used to implement popular Internet services: email clients, graphic and text editors, instant messengers, data storage and social networks. Some SaaS services are in demand in the corporate segment exclusively, such as video conferencing programs, ERP and CRM systems, project or group management services, and website builders.
SaaS examples: Gmail, Dropbox, SAP, MailChimp, Zendesk, Canva, SalesForce, WordPress, Cisco WebEx.
SaaS is a kind of all-in-one service: provider thereof is fully responsible for preparing and maintaining IT infrastructure, both at physical and software levels.
Benefits of using SaaS
- This is the simplest, most understandable and user-friendly cloud service model.
- The provider is entirely responsible for ensuring cloud service operability
- It is the most convenient solution for small and medium-sized enterprises which have to solve typical IT tasks in 99% of cases.
- Saving on payroll for developers, network engineers and system administrators.
The table contains the most important points about three popular cloud models:
| IaaS Virtual IT infrastructure | PaaS Cloud environment with a set of development tools | SaaS Fully ready-made cloud product for the end user |
| Internet shops, ticketing and other online services, database hosting, arranging remote office work. | Hosting databases, analytical systems, big data processing systems, ML, IoT | Messengers, planners, blog platforms, mail services, data storages, text, graphic and other editors, CRM/ERP, other business automation tools. |
| A pool of computing resources for deploying an IT infrastructure Quick start from scratch Flexible allocation of resources on demand Inexpensive solution for startups and SMBs Perfect for businesses that have surges in demand | Ready-to-use development tools Saving time on infrastructure configurations Fast development, testing and delivery of applications | Environment that is fully ready to carry out business tasks The provider is responsible for service development, deployment and support The vast majority of services run directly from the browser Perfect for projects requiring simple and affordable solutions |
All these service delivery models are cloud-based. Our experts can help you choose the best cloud solution tailored for specific business requirements, as well as learn about other Colobridge platform features that will help make your IT infrastructure even more fault-tolerant and efficient.





